Modern technologies, especially the internet, have indeed made it easier for businesses to reach global markets. E-commerce platforms, digital marketing tools, and advanced logistics solutions allow even small businesses to sell products regardless of distance. The promise of global accessibility suggests such market potential and increased sales opportunities that literally every product is expected to be globally available.
Despite these opportunities, global commerce isn’t always the optimal approach for every business, especially when considering the following challenges:
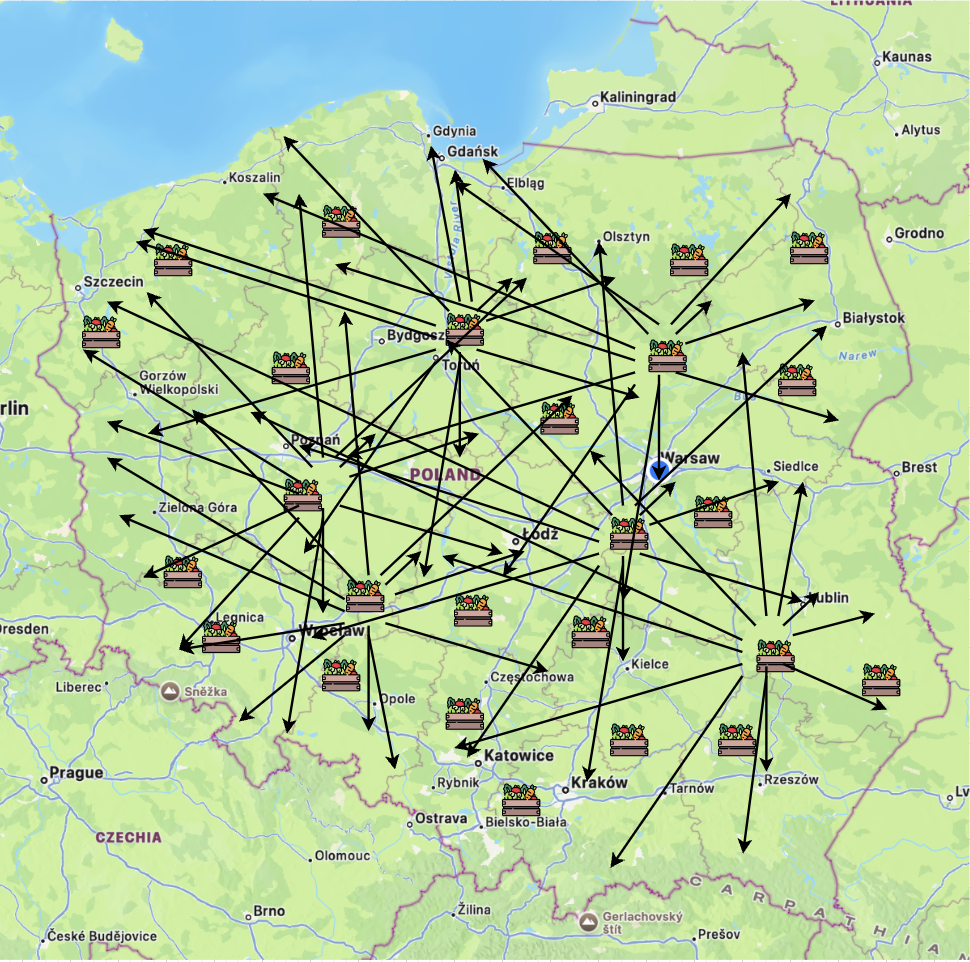
- Logistical Complexity: Longer supply chains prone to delays, disruptions and a product spoilage. That can significantly increase operational costs and complexity. Promising same delivery conditions to different regions becomes even more expensive and fragile offer.
- Environmental Impact: Global shipping contributes to a considerable carbon footprint due to the emissions associated with transporting goods over long distances. This aspect of global commerce is increasingly at odds with growing consumer demand for sustainable practices.
- Marketing: Tailoring marketing strategies to different cultural, linguistic, and demographic contexts can be resource-intensive. Missteps in understanding local consumer behavior can lead to failed marketing efforts and poor sales.
- Economic Inefficiency: While global reach expands the market, it also dilutes focus and can lead to inefficiencies in targeting and conversion. Local markets often have specific needs and preferences that global campaigns might not address effectively.
What would be if every e-commerce project would go global first:
Localized distribution approach
On the other hand, given these challenges, a localized distribution approach can make more sense for certain businesses, particularly those involved in the production and sale of goods like fresh food, handmade products, or other items best consumed close to their point of production. Here’s why a focus on local markets can be advantageous:
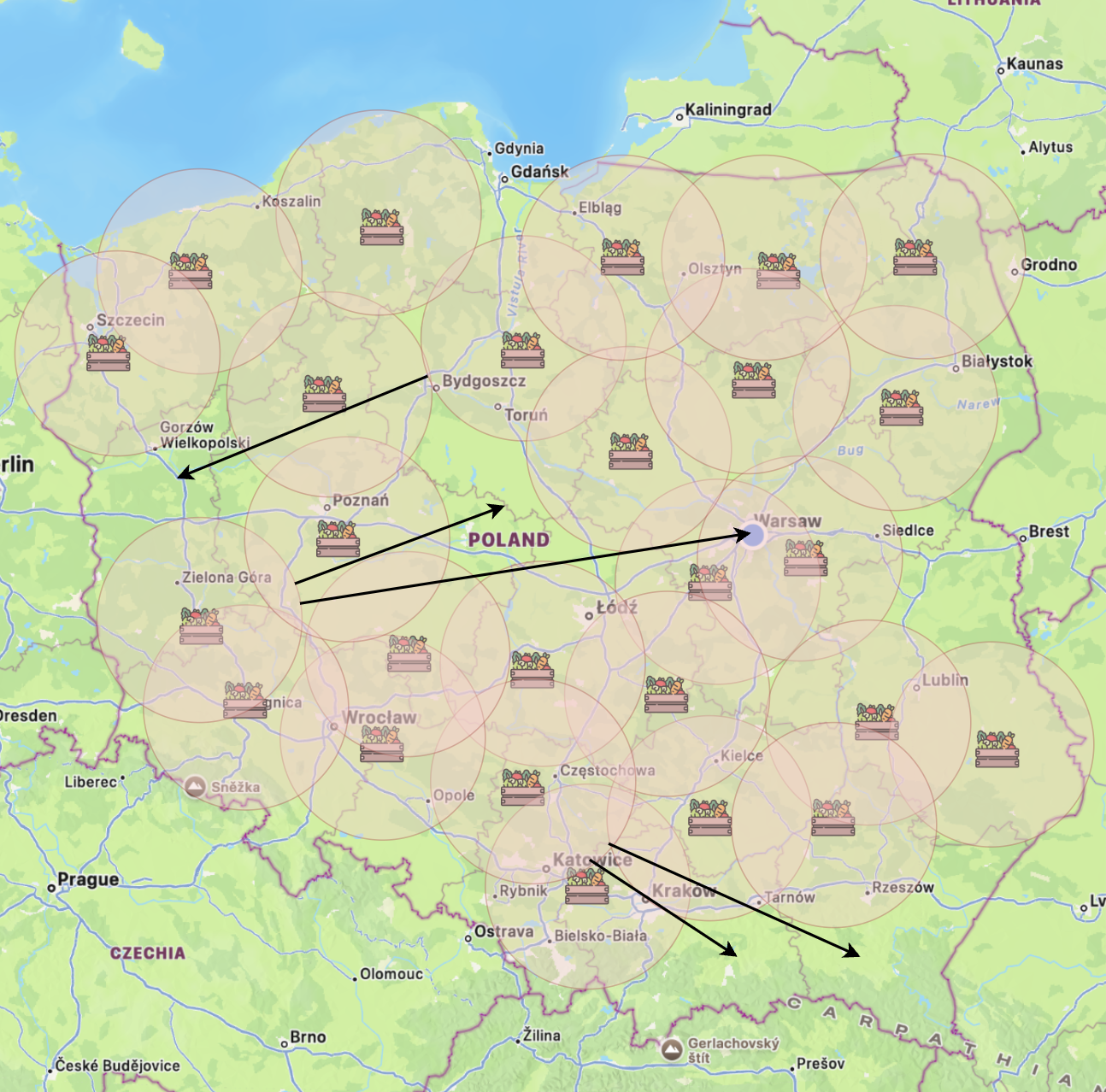
- Simplified logistics: Reduced delivery price due to shorter distances and overall logistics simplicity.
- Enhanced Community Engagement: Local businesses can build strong relationships with their customers, fostering loyalty and repeat business. These relationships are based on personal interaction and a shared community identity.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Shorter supply chains mean less transportation is required, which not only reduces logistics costs but also lowers the environmental impact of shipping goods.
- Supporting Local Economies: By focusing locally, businesses help to circulate money within the community, supporting local employment and contributing to the local economy’s resilience.
The approach proposed by Fairr. Every producer and reseller focused on its nerest region first, still being able to fulfill orders from any other region:
Conclusion
While global commerce is undoubtedly a future-facing concept enabled by technological advancements, it’s not universally applicable or sustainable for all business models. In many cases, focusing on local markets provides more sustainable, community-oriented, and economically viable options. This balanced approach acknowledges the benefits of global reach but also respects the practical limitations and environmental considerations of such expansion.